What is prompt engineering?
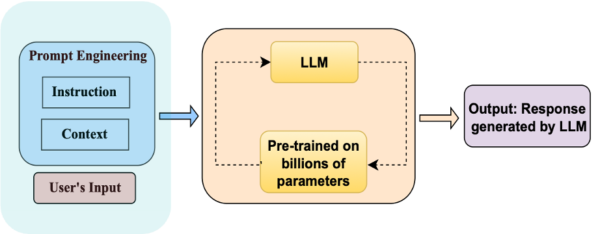
In this post, we are going to explore the fascinating concept of Prompt Engineering, a key component in the field of artificial intelligence. Prompt Engineering involves developing inputs that guide large language models or LLMs, to generate desired outputs (see figure 1). The quality and structure of these prompts significantly influence the efficiency and accuracy of the responses that we obtain from AI systems.

The post will cover the foundational aspects of what makes a prompt, the role of context and instructions in shaping these prompts, and how they interact with user interfaces.
What is a prompt?

Moving into more specifics, let’s define what a prompt actually is. In the simplest terms, a prompt is a text or instruction given to a LLM to get its responses (see figure 2). For instance, asking LLM ‘Tell me about the Galaxy’ is a prompt, but it is quite broad and can lead to varied responses.
However, if we refine this to ‘Could you elaborate the process of stars formation by considering gravitational role?’, we ask the LLM to focus on specific scientific details which can enhance the relevance and depth of the response. This show how important precision and context are in prompt design.
How a prompt works?

Let us look at the mechanics of how a prompt works within a LLM (figure 3). When a user inputs a prompt, the large language model processes this input by analyzing the text and context provided. The model then generates a response based on its training and the specific instructions embedded within the prompt. This step-by-step processing highlightes the importance of clear, well-designed prompts in achieving meaningful LLM interactions.
Why is prompt design important?

Why invest time in designing effective prompts? Firstly, well-developed or created prompts produce more accurate and to-the-point answers that use the full creative and technical potential of LLMs. Additionally, they save time and reduce the misunderstandings or irrelevant outputs. This makes prompt design not just a technical skill but a necessary practice for anyone looking to use LLM effectively (see figure 4).
Key elements of prompt engineering

There are four key elements in prompt engineering: clarity, context, constraints, and the balance between creativity and precision (see figure 5). Each of these plays a important role in how effectively the AI understands and responds to the prompt. By integrating these elements, we can make prompts that are not only clear and concise but also rich in context and appropriately bounded by constraints, whether those are word counts, specific topics, or the type of response expected.
Prompt examples
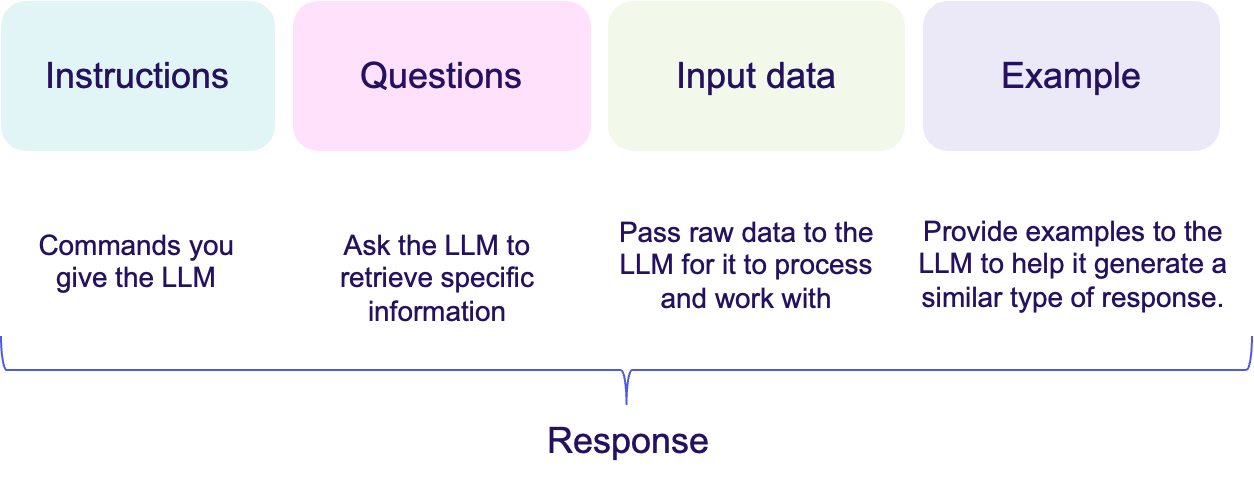
Let’s consider some basic prompt examples to illustrate different approaches (see figure 6 and 7). For example, combining instructions with a question can guide the LLM to follow a specific rule while addressing a related query. This method is excellent for focused responses.
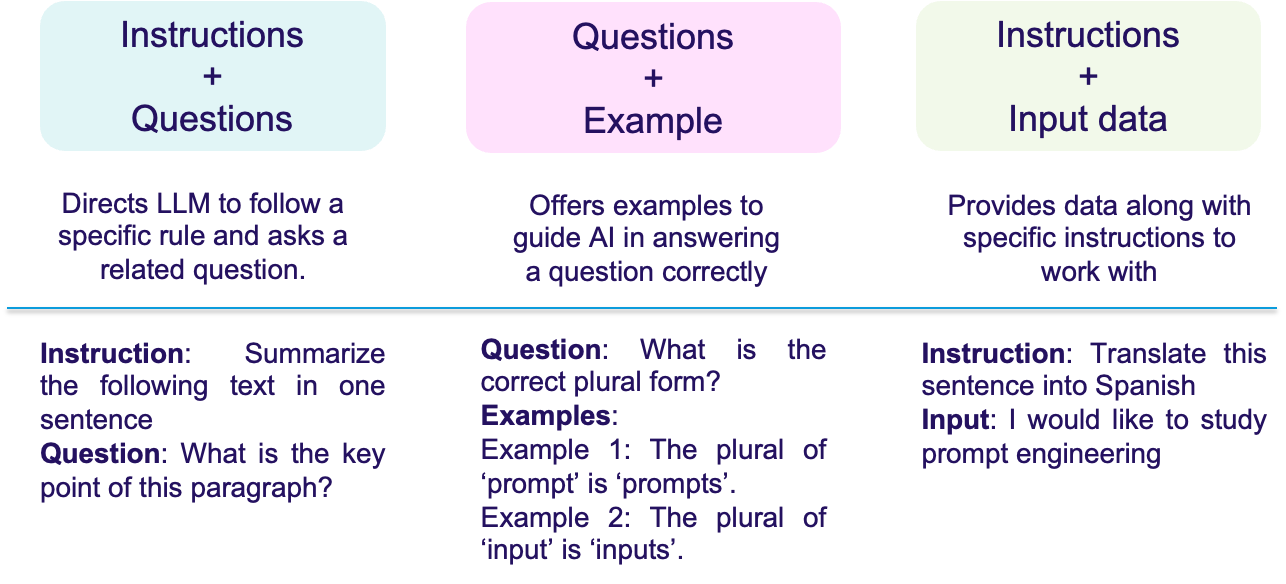
Similarly, including examples within your prompt can help the AI model to understand the context better and produce more accurate answers, especially in tasks requiring nuanced understanding.
How information is processed?
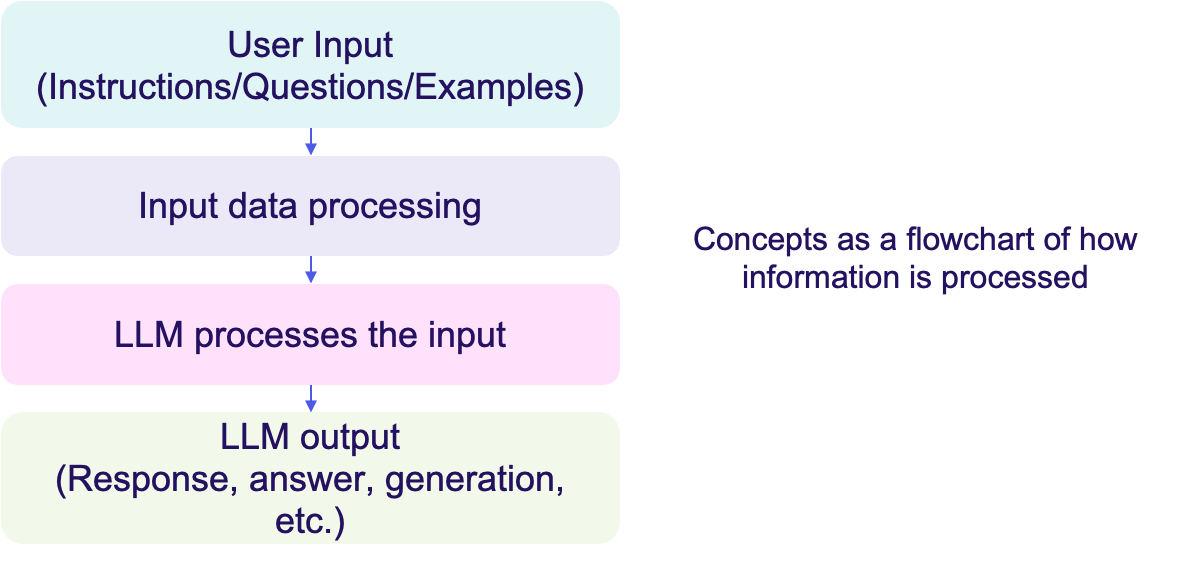
Understanding the flow of information within an LLM model helps in designing effective prompts. When we input instructions, questions, or examples, the LLM processes these based on its programming and training. The outcome is a generated response that ideally meets the user’s needs. This process focuses on the importance of our input in shaping LLM outputs, making prompt design a key skill.
Conclusion
Mastering prompt engineering allows us to tackle the full capability of LLMs. Practical implementation of these concepts can dramatically improve how we interact with LLM, whether for business applications, academic research, or personal use.
That is it! Thank you!
You can visit the geneative ai playlist for other interesting reads: https://ai-researchstudies.com/category/generative-ai/
Happy reading 🙂 See you in the next post!